

Photodiodes are generally recognised as a semiconductor device that has the ability to absorb light energy in order to generate electric current.
For this specific reason, such device often has different names like photo sensor or photo-detector. The main purpose of developing such an application is to use these in a reverse-bias condition.
Based on this concept, this tutorial is intended to include information regarding the types and applications of photodiodes along with explaining the advantages and disadvantages of it as well.
On a very basic note, a photodiode can be defined as a diode that has a PN-junction, consumes light or photonic energy, and has the ability to convert this photo energy to the electric current. As the main action of these devices is to absorb photo or light energy, they are made to be sensitive toward the light that enabling the photodiodes to easily convert the light energy to the electrical one (Elprocus.com, 2022).
One of the best examples of the application of photodiodes is the Solar cell as these are made to convert the solar or light energy to an electric one.
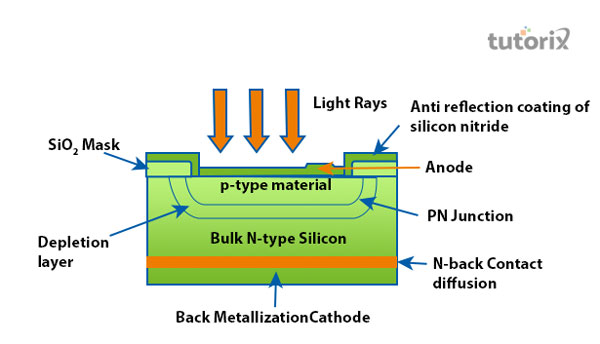
Figure 1: Construction of the Photodiodes
The construction of photodiodes is done by using two types of semiconductors such as N-type and P-type.
The diffusion of P-type substrate that is lightly adopted is responsible for the formation of the material that is P-type. This diffusion method helps in the formation of the P+ ion layer.
The epitaxial layer of N-type ios is grown for the substrate of N-type (Elprocus, 2022). Over the heavy doped epitaxial layer of N-type, the P+ diffusion layer is developed. The contacts are made of metal to act as an anode and cathode. The front part of the diode is separated into non-active and active surfaces. The design beholds by the non-active surface is done with silicon dioxide.
Technologically several types of photodiodes are used as the devices offer different properties. The types of photodiodes are as follows:
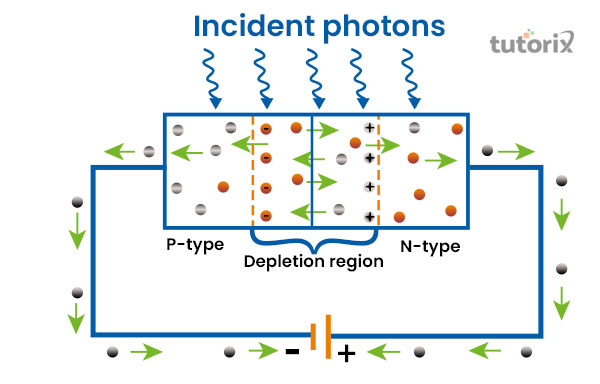
Figure 2: PN Photodiodes
This version is considered the first developed form of photodiodes. Being the first mode, its performance has no such development as other versions showcase. For this particular reason, at the present time, the application or usage of this type of photodiodes is lesser than other forms of it.
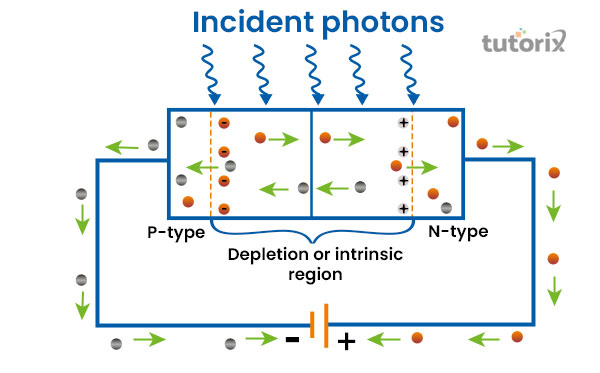
Figure 3: PIN Photodiodes
This form of photodiodes is the most widely used form of photodiodes in the present day. This form shows more efficiency in absorbing light photons in comparison to the standard PN photodiodes (Physics-and-radio-electronics, 2022). The wide intrinsic area that is provided between two regions P and N allows more lights to be collected.
The usage of such kinds of photodiodes is generally seen in the area where the light is comparatively low as these forms have a high level of gain. Besides having high power of collection, the device creates a high range of noise as well. For this particular reason, this version is not widely used or available for use for any purposes.
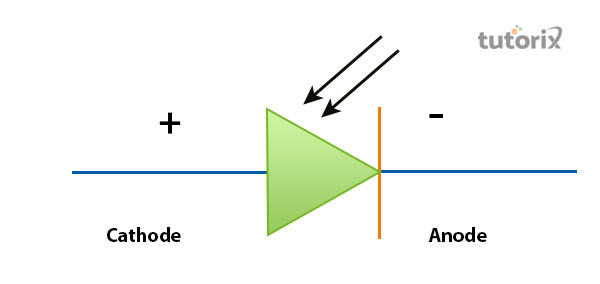
Figure 4: Symbol of Photodiodes
The symbol of photodiode are usually developed by utilising the symbol of the basic diode where two arrows have added that point towards the device. The two added arrows are the symbol that indicates the direction of light that strikes the device (Etechnog, 2022).
The above figure showcases the symbol of photodiodes that shares a similarity with the construction of the Light-emitting diode where one difference can be spotted as the arrows are pointed in the opposite direction.
The main application of photodiodes is the conversion of the photon or the light energy into an electrical current. Based on this basic purpose, the other applications are as follows: The photodiodes have a simple day-to-day application for the linear response the devices are offered to light illumination. Another application of photodiodes is in the detection circuit (Aslan et al. 2019). For providing electronic isolation, this technology is used in helping opt couplers. Moreover, for the exact measurement of Light's intensity, photodiodes are used. It has other medical applications and logic circuits as well.
One of the advantages that photodiodes provide is better frequency response. Along with that, a photodiode also offers better spectral response and linearity as well. In order to laser pulse shape, photodiodes are considered one of the most suitable instruments (Electronics-notes, 2022). The operation of this device can be done at a high-frequency level that is 1 MHz. moreover, the form of photodiodes is generally used as a variable resistance device as the high sensitivity it shows to light. The majority of the forms of such device has less noise with the technological advantage of being a faster photo director.
The disadvantages that photodiodes behold are few in comparison to the advantages photodiodes offer. The device has a rapid increment of dark current in relation to temperature. Another reason for this is the small active area allowed for the devices. Moreover, it has a technical requirement that is offset voltage with application in low irradiance.
The focus of this tutorial is focused on the explanation of the information regarding photodiodes and the various applications it has in the present day. This tutorial has included further information that showcased that photodiodes are classified into three major types. Along with explaining all three kinds of photodiodes, the tutorial further focused on exemplification of how the construction of photodiodes is made. In this section, it has been seen that the construction of photodiodes has been made by following the reverse-bias-condition means which means the p-side of photodiodes is connected to the negative terminal of the battery whereas the positive terminal is connected to the n-side.
Q1. What is the working principle of photodiodes?
The main principle based on which the photodiodes work is the principle of photo electronic effect. The operating principle of this circuit shows that the moment illumination is seen on the junction where two terminals of semiconductor meet, the flow of electric currents starts at that point.
Q2. What difference is shared between LED and photodiodes?
The technology that is used in these two things is reverse of each other. LED has the power of generating lights with the help of carriers that are charged whereas photodiodes have the ability f generate current for the presence or by absorbing photons. In more simple words, it can be stated that LED converts current to light energy and the main purpose of Photodiodes are to convert light energy to electrical current.
Q3. Do photodiodes emit light?
A direct band-gap photodiode generally emits light. By loading it in a direct manner, the modulation of the amount of light can be done. By measuring the amount of shin light above the band-gap energy on an III-V junction, carriers can be made.
Q4. Is a solar cell a photodiode?
As solar cell converts photons to electric current, solar cells are considered large-area-photodiode.
Aslan, N., Koç, M. M., Dere, A., Arif, B., Erkovan, M., Al-Sehemi, A. G., ... & Yakuphanoglu, F. (2018). Ti doped amorphous carbon (Al/Ti-a: C/p-Si/Al) photodiodes for optoelectronic applications. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1155, 813-818. Retrieved from: https://pure.port.ac.uk
Electronics-notes.com, 2022. Photodiode Technology. Retrieved from: https://www.electronics-notes.com/articles/electronic_components/diode/photodiode-detector-technology.php [Retrieved on 8th June 2022]
Elprocus.com, (2022). What is a Photodiode: Working Principle & Its Characteristics. Retrieved from: https://www.elprocus.com/photodiode-working-principle-applications/ [Retrieved on 8th June 2022]
Etechnog.com, 2022. Photodiode Symbol, Diagram, Circuit, Characteristics. Retrieved from: https://www.etechnog.com/2021/06/photodiode-symbol-diagram-circuit.html [Retrieved on 8th June 2022]
Physics-and-radio-electronics.com, (2022). Photodiode. Retrieved from: https://www.physics-and-radio-electronics.com [Retrieved on 8th June 2022]