

The human evolution from early humans to modern ones underwent several changes. This process witnessed different lifestyles of humans. They advanced from huntergatherers to food producers. They discovered many things which are still in use in a modified version. Subsequently, with the development of farming, they began to develop shelters for an extended stay in a place. Initially, they are believed to have originated in Africa and slowly spread to other parts of the world. Earlier these people lived in small groups and then shifted to large ones. With that, the concept of villages was formed and cultural adaptation became easier.
Humans initially led the life of hunter-gatherers. And they used stone weapons for hunting wild animals and gathering from trees on their way while moving.
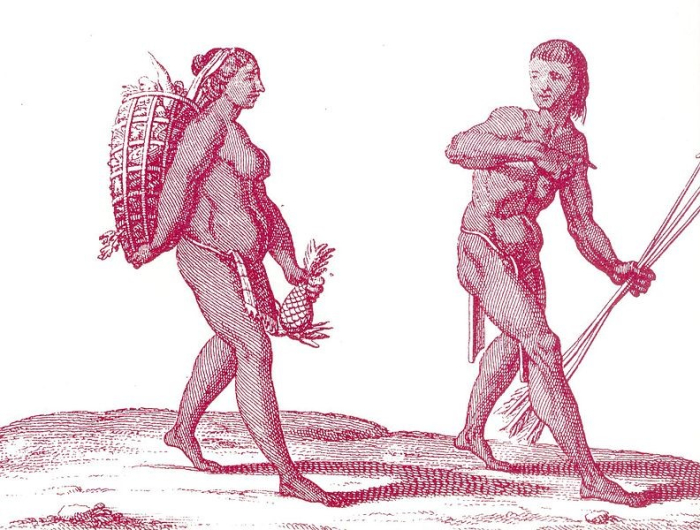

Pierre Barrère, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
They used to cover themselves either with tree produce like leaves or barks or animal skins in order to keep them safe from climatic conditions.
With time they discovered fire and started using it for different purposes.
Over the years when the climate became warmer, early modern humans began to move towards farming. Now some of these were involved in intensive hunting and others were in the initial stage of domestication.
Early modern humans cultivated crops and grew crops like corn, wheat, and barley. Now they have become food producers.
As they started living in small groups, the concepts of family and communities also emerged. This in turn led to the formation of villages for cooperation and protection.
Historians and researchers dated back the origin of early modern humans i.e., Homo sapiens in different parts of Africa from 200,000 to 100,000 years ago. For many years these modern humans continued to behave like their old-fashioned predecessors by making crude and rudimentary stone tools.
Scientific researchers asserted that there was a gap between when humans began to look modern and when they began to behave modern. According to Stephen Shennan (an archaeologist at London University), it was due to cultural upheaval that humans interacted with others and started living in big groups, which paved the way for their modernization.
The rise in population in Africa made it easier for people to develop contact with neighbouring communities. Probably they exchanged mating partners. Subsequently, this led to the interchange of ideas and genes. Hence, set the stage for new creations and inventions.
Around 45,000 years ago Homo sapiens began to migrate from Africa to Europe. In Europe, Neanderthals were already there when the species of modern humans arrived. Gradually they outnumbered their rival Neanderthals by eliminating them from there.

DataBase Center for Life Science (DBCLS), CC BY 4.0
During 25,000 years ago during the Ice Age, when the ice began to cover almost all of the northern part of Europe, the number began to decline. But at the end of this age, the population again rose up.
11,000 years ago with the advent of farming and settled life female fertility also increased. As a result of this, the population reached up to 6 to 7 million on the eve of the Neolithic period.
In contrast to previous research, new reports show at the human population expanded during the hunter-gatherer period.
Some archaeological reports indicated that human population expansion owes to the Neolithic period. In this period the shift to domestication led to the development of more advanced techniques of agriculture and settlements paving the way for population expansion from 4-5 million to 60-70 million.
This theory of population expansion was negated by recent researchers. A study was conducted by the university of Paris, in which they concluded that the population was expanded much before the farming or Neolithic period; rather this expansion can be associated with the Palaeolithic times of hunter-gatherers.
Although these recent researches do agree with the fact that those who adopted farming a little early did witness the rapid expansion of the population, another way the population expansion in the Palaeolithic period paved the way for the transition from gatherers to farmers.
Initially, modern humans preferred to stay in small groups but gradually they started moving into large groups, which were made through reciprocal connections. In these groups they had collective access to resources be it tools or food. The concept of personal or individual control was missing till the time. They used to pose threats to other groups. All of these things began to change and became more modernized when the large groups transformed into villages and slowly the concept of the family also came into being.

Nazgul02, CC BY-SA 3.0
Mladec caves are in the Prague region in modern day the Czech Republic. These caves contain many remains or skeletons of early modern humans. It is also considered the world’s oldest “village’’. The bones found here dated back 31,000 years back. Researchers tried to analyse the DNA of these fossils but were unable to extract the usable one Somehow they managed to analyse the DNA of two specimens but get to know those did not belong to the series of “homo”.
There have been different research has been made to analyse the lifestyle, culture, and population expansion of early modern humans in the process of evolution. As early modern humans started moving to different parts of the world they began to adapt to different surroundings and environments in different ways. Because of the changing climate, different ways of life could be seen. Over a period of time, they could find a lot of food in a relatively small area. This made people stay in a place for a longer period of time. This led to a shift from nomadic life to a settled one.
Q1. Which place in India the remains of early humans have been found?
Ans. The traces of early humans in India have been found in the Bhimbetka rock shelter, which is located in Madhya Pradesh.
Q2. Which phase of ancient times did the stone ages belong to? What are the sources to know about that time?
Ans. The history of early humans and the Stone Age is part of prehistory, for which we do not have written records. And all the information we get to know about this period is purely from archaeological sources of history like artefacts like bones, cave paintings and fossils etc.
Q3. When and how was fire discovered?
Ans. The fire was discovered in the Palaeolithic age. It is believed that humans might have witnessed naturally caused fires like lightning or forest fire. Then with their observation and experimentation, they must have learned to rub two dry stones to produce sparks of fire.
Q4. Mention the uses of fire for early humans.
Ans. Fire was used by early humans for −
Cooking meat
lightening caves or surroundings
Scaring away animals
Keeping the place warm to protect themselves from the cold.
Q5. Who were Neanderthals?
Ans. The neanderthals belong to the family homo they followed the evolutionary path of humans after homo erectus. With the increase in their brain, they were the ones who began the concept of cultural adaptations.