

Healthcare in India is a complex topic that spans both the public and private sectors. In this tutorial, we will discuss the role of the government in healthcare in India, from providing healthcare subsidies to regulating medical practices.
India has a population of over 1.3 billion people and is the world's second-most populous country. The country is also home to many different religions, languages, and cultures. As a result, healthcare in India is complex and diverse.
Government plays a significant role in healthcare in India. Indian government provides healthcare services through its public health services, which are administered by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. The government also operates several hospitals and health clinics that provide healthcare to the general public and certain groups, such as the military and the poor. In addition, the government provides health insurance for citizens and subsidizes the cost of medical treatment for those who cannot afford it.
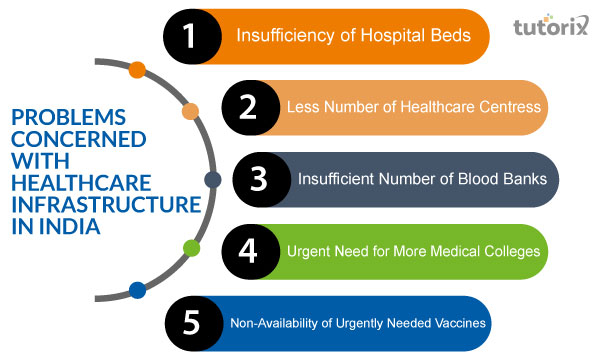
Figure: Problems concerned in healthcare infrastructure in India
The Indian healthcare system is decentralized and fragmented, with a variety of private clinics, hospitals, and nursing homes operating side-by-side with public facilities. There is inconsistency in quality across facilities, and patients have little choice in which doctor they see or which hospital they go to. The overall level of care provided is poor compared to other developed countries, and there are significant costs associated with accessing healthcare in India.
Despite these challenges, the Indian healthcare system is growing rapidly thanks to increasing income levels and greater awareness among the population of the importance of healthcare.
India's healthcare system is one of the most diverse in the world. It is overseen by the government, which has a large role in setting policy and funding healthcare initiatives. The government also regulates healthcare providers and sets standards for quality. This system has been controversial, though, because it can be expensive and difficult to access. There are also reports of corruption in the healthcare system.
When it comes to healthcare, India takes a central planning approach. This means that the government sets broad goals and instructs healthcare providers what they need to do to meet those goals. The government also sets prices for health services, which can be expensive for consumers.
In contrast, most countries in the world use a market-based approach. This means that the government allows free competition between healthcare providers, and consumers can choose the provider that best meets their needs. Market-based approaches generally result in better quality healthcare because providers are forced to compete for customers
The private sector plays a significant role in India's healthcare system. There are several private hospitals and clinics, as well as private health insurance schemes. The private sector has been criticized for charging high fees and providing poor quality care. In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of private hospitals that are providing good quality care at reasonable prices
The majority of Indians get their healthcare through government-run hospitals and clinics. These facilities are generally affordable and accessible, but they can be crowded and poorly equipped. Many people also use traditional medicine to treat illnesses.
As mentioned earlier, there is also a large private sector in India, which provides healthcare services. These companies often charge high fees, but they have been accused of providing substandard care
In India, healthcare is a state subject. The government has a major role in healthcare, through its control of the health system and its funding. Healthcare in India is largely free and accessible, but there are many problems with the quality of care and the availability of resources.
The government of India plays a significant role in the healthcare sector. India has one of the largest populations in the world, and its citizens need access to quality healthcare. The government of India plays a key role in funding healthcare initiatives, as well as improving accessibility and quality of care.
One aspect of the government's role in healthcare is ensuring that all Indians have access to basic health services. The National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) is a key program that helps to achieve this goal. NRHM provides rural Indians with access to essential health services, such as primary healthcare, maternal and child health care, and pandemic response measures. In addition, the NRHM provides financial assistance for hospitals and clinics that provide medical services to rural Indians
The government of India also plays a critical role in funding healthcare initiatives outside of India's borders. For example, the India Global Health Initiative (IGHI) funds healthcare projects overseas that aim to improve public health outcomes. IGHI has funded projects in Nigeria, Nepal, and Haiti. These projects have helped to reduce rates of disease spread and improve public health outcomes
Overall, the government of India plays an important role in facilitating access to quality healthcare for its citizens
In recent years, the government of India has made strides in improving healthcare for its citizens. The government plays a significant role in the health sector in India. The main focus of the government is to provide healthcare for all citizens and to improve the overall quality of life. To achieve this, the government has invested substantially in the health sector over the years. This has led to increased access to health services for all citizens, as well as improved quality of care. There are still areas where the government could improve its efforts, but overall it has made considerable progress in improving healthcare in India
The Affordable Healthcare Act (AHCA), which was signed into law by President Donald Trump, is a major step forward in this regard. The AHCA aims to reduce the cost of health care and make it more accessible to all Americans, including those living in India. By doing so, the AHCA will help to improve healthcare access and quality for Indians living in the United States
Q1. What are the different ways through which the government can provide healthcare to all?
Ans: The government has developed several programs to provide access to common health issues. Universal Health Coverage Scheme (UHC) is one such program that provides healthcare coverage for Indians. UHC covers preventive services like periodic check-ups and treatment of preventable diseases/ailments.
Q2. What is health? Explain the factors that affect health?
Ans: Health is a state of freedom from disease and injury, wellbeing, bodily integrity, and the ability to carry out day-to-day activities without undue physical or mental strain. The factors that affect health may include physical or mental health, the social sphere maintaining and promoting health, access to good food and water, sanitation, and more.
Q3. What are the improvements in healthcare facilities in India?
Ans: Over the last decade, India has seen significant improvements in healthcare facilities. The country has made remarkable progress in health care and public health services, both in terms of infrastructure and availability of providers. There are over 200,000 healthcare facilities across India with more than 3400 hospitals (public and private), 655 nursing homes, 177 wellness centers, 82 hospices, 50 rehabilitation centers (specialized medical institutions for physically challenged patients), and 875 primary health clinics.
Q4. Write some of the negative aspects of our healthcare system?
Ans: There are several features of India's healthcare system that can be viewed as negative, such as the following: a lack of affordable and high-quality health care facilities, an estimated 796 million people still without access to complete primary health care, workplace accidents causing injury to 338,475 workers in 2009-10, and a large number of communicable illnesses caused by poor sanitation.
Q5. Give an account of the position of healthcare services in India?
Ans: Healthcare in India is regulated by the government. Public health services are run by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and they provide healthcare services mainly to the general public. The government operates hospitals, emergency centers, and primary health clinics that serve certain groups as well. Education on healthcare is also provided through school curricula and teacher's guides.
Q6. What do we need to prevent and treat diseases?
Ans: The population in India faces the challenge of a high level of infectious and communicable diseases, which can be prevented with immunization and hygiene. For our country to prevent and treat diseases, we need to understand the way diseases are spread. We also need to understand how public health affects different people and take proper action according to their needs. The government plays a significant role in healthcare in India by launching awareness programs about certain diseases, providing healthcare services for those who need them, and launching preventive measures against these diseases so that we encounter