-
Introduction to Biological Classification
-
History of Biological Classification
-
Three and Four Kingdom Systems
-
Five Kingdom System
-
Three Domains of Life
-
History of Plant Classification
-
Kingdom Monera
-
Bacteria – Size, Shape and Arrangement
-
Bacterial Cell Envelope
-
Bacterial Cytoplasm
-
Bacterial Cell Surface Structures
-
Nutrition in Bacteria
-
Respiration in Bacteria
-
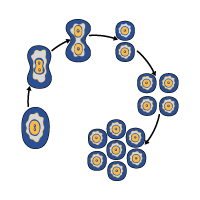
Reproduction in Bacteria
-
Archaebacteria: The Oldest Bacteria
-
Cyanobacteria: The Blue-Green Algae
-
Mycoplasma: The Wall-Less Bacteria
-
Gram Staining of Bacteria
-
Structure of Virus
-
Types of Viruses and Viral Diseases
-
Reproduction in Viruses
-
Viroids, Prions and Virusoids
-
Introduction to Kingdom Protista
-
Chrysophytes: The Golden Algae
-
Pyrrophytes: The Fire Algae
-
Euglenoids: The Photosynthetic Protists
-
Slime Moulds: The Saprophytic Protists
-
Protozoans: The Heterotrophic Protists
-
Flagellated Protozoans
-
Amoeba: The Amoeboid Protozoans
-
Amoeboid Protozoans and Their Orders
-
Sporozoans: The Parasitic Protozoans
-
Ciliated Protozoans
-
Kingdom Fungi
-
Vegetative and Asexual Reproduction in Fungi
-
Sexual Reproduction in Fungi
-
Types of Sexual Reproduction in Fungi
-
Classification of Fungi
-
Phycomycetes – Oomycetes and Zygomycetes
-
Importance and Diseases of Oomycetes and Zygomycetes
-
General Features of Ascomycetes
-
Importance of Ascomycetes
-
General Features Basidiomycetes
-
Importance of Basidiomycetes
-
General Features and Importance of Deuteromycetes
-
Lichens and Mycorrhiza
-
Introduction to Plant Kingdom
-
Thallophyta (Algae) – General Features and Importance
-
Rhodophyceae (Red Algae)
-
Examples and Importance of Red Algae
-
Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae)
-
Examples and Importance of Brown Algae
-
Chlorophyceae (Green Algae)
-
Examples of Green Algae – Chlamydomonas
-
Examples of Green Algae – Volvox
-
Examples of Green Algae – Ulothrix, Spirogyra and Chara
-
General Features of Bryophytes
-
Bryophytes – Liverworts (Marchantia)
-
Bryophytes – Mosses
-
General Features of Pteridophytes
-
Reproduction in Pteridophytes
-
Types of Pteridophytes
-
Importance of Pteridophytes
-
Pteridophytes – Selaginella
-
Difference Between Bryophytes and Pteridophytes
-
General Features of Gymnosperms
-
Reproduction in Gymnosperms
-
Types of Gymnosperms
-
General Features of Angiosperms
-
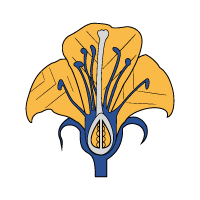
Life Cycle of Angiosperms
-
Problems on Plant Kingdom
-
Introduction to Animal Tissues
-
Main Features of Epithelial Tissues
-
Specialised Structures and Junctions
-
What Are Simple and Stratified Epithelial Tissues?
-
Squamous Epithelium
-
Cuboidal Epithelial Tissues
-
Columnar Epithelium
-
Pseudostratified and Transitional Epithelium
-
Glandular Epithelium
-
What Is Connective Tissue?
-
Cells of Connective Tissues
-
Fibres of Connective Tissue
-
Loose Connective Tissue – Areolar and Adipose
-
Dense Connective Tissue
-
Skeletal Connective Tissue – Cartilage
-
Skeletal Connective Tissue – Bones
-
Internal Structure of Bone
-
Differences Between Bone and Cartilage
-
What Are Muscle Tissues?
-
Striated or Skeletal Muscular Tissue
-
Unstriated or Smooth Muscular Tissue
-
Cardiac Muscular Tissue
-
Cells of the Nervous Tissue
-
Structure of a Nerve
-
Vascular Connective Tissue
-
Earthworm – Introduction and Body Wall
-
Earthworm – Morphology
-
Earthworm – Digestive System
-
Earthworm – Blood Vascular System
-
Earthworm – Respiratory and Excretory Systems
-
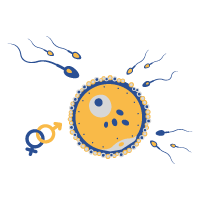
Earthworm – Reproduction
-
Earthworm – Nervous System and Economic Importance
-
Cockroach – Introduction and Body Wall
-
Cockroach – Morphology
-
Cockroach – Digestive System
-
Cockroach – Blood Vascular System
-
Cockroach – Respiratory and Excretory Systems
-
Cockroach – Nervous System
-
Cockroach – Reproductive System
-
Frog – Introduction, Morphology and Body Wall
-
Frog – Digestive, Respiratory and Blood Vascular Systems
-
Frog – Excretory, Nervous and Reproductive Systems
-
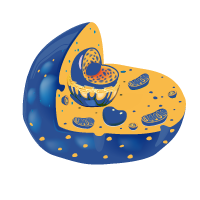
Introduction to Cell
-
Shape, Size and Types of Cells
-
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
-
Cell Membrane: The Outer Cover of the Cell
-
Membrane Transport – Passive Transport
-
Membrane Transport – Active Transport
-
Membrane Transport – Bulk Transport
-
Cytoplasm: The Ground Material of the Cell
-
The Endomembrane System and ER
-
Golgi Apparatus: The Post Office of the Cell
-
Lysosomes: The Suicidal Bags of the Cell
-
Vacuoles: The Storage Bodies of the Cell
-
Role of the Endomembrane System
-
Mitochondria: The Power House of the Cell
-
The Cytoplasmic Microbodies
-
Ribosomes: The Protein Factories of the Cell
-
Cytoskeleton – Microfilaments
-
Cytoskeleton – Intermediate Filaments
-
Cytoskeleton – Microtubules
-
Flagella and Cilia
-
Centrioles and Centrosome
-
Nucleus: The Brain of the Cell
-
Introduction to Chromosomes
-
Types of Chromosomes
-
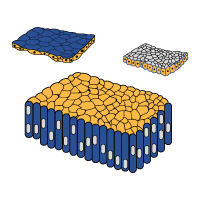
Introduction to Cell Wall
-
Structure of Cell Wall
-
Introduction to Plastids
-
Chloroplast: The Kitchen of the Cell
-
Differences Between Plant Cells and Animal Cells
-
Differences Between Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic Cells
-
Introduction to Biomolecules
-
Bonding in Biomolecules
-
Protein Monomers: The Amino Acids
-
Peptides and Protein Primary Structure
-
Secondary Protein Structure
-
Protein Tertiary and Quaternary Structures
-
Functions of Proteins
-
Carbohydrates: Classification and Function
-
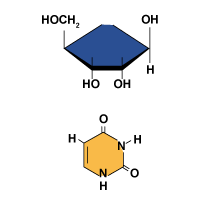
Carbohydrate Monomers: The Monosaccharides
-
Glycosidic Bond and Disaccharides
-
Polysaccharides: General Introduction and Types
-
Homopolysaccharides: Cellulose, Starch and Glycogen
-
Some Other Polysaccharides
-
Nucleic Acid Structure
-
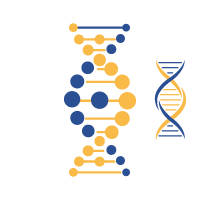
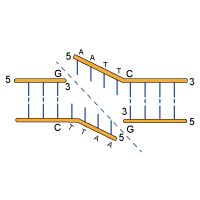
Structure of DNA
-
RNA and Its Types
-
Lipids: General Introduction and Function
-
Lipids Formation and Structure
-
Phospholipids, Sphingolipids and Glycolipids
-
Steroids and Lipoproteins
-
Enzymes and Their Properties
-
Nomenclature and Classification of Enzymes
-
How Do Enzymes Catalyse Reaction?
-
Models for Enzyme Action
-
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
-
Enzyme Inhibition
-
Cofactors and Coenzymes
-
Primary Metabolites and Secondary Metabolites